Are you aware that November is Diabetes Awareness Month and that November 14 is World Diabetes Day? Diabetes is a prevalent disease in Canada. More than one-quarter of Canadians (10,756,00 or 28% of the population) are living with diabetes or prediabetes, and that number is expected to increase to 32% of the population by 2028. Individuals who have diabetes cannot properly generate or respond to the hormone known as “insulin,” which translates to elevated levels of glucose in the patient’s urine and blood. If you are a diabetic, you are aware that the disease can harm your eyes, nerves, kidneys, heart and other vital systems in the body. However, did you know it can also cause problems in your mouth, your smile and your oral health?
So what exactly does diabetes have to do with your Oral Health? More than most people would expect.
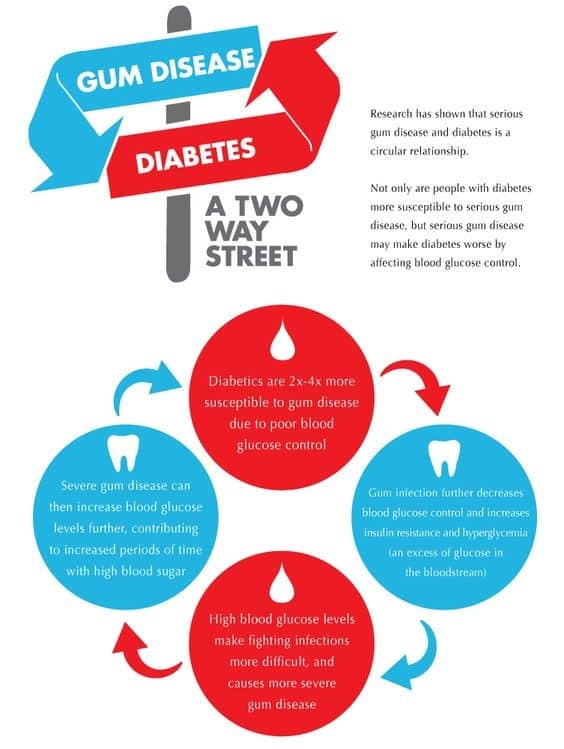
Diabetes and Gum Health Have Direct Correlation, called Two-Way Street
According to studies, there is a strong correlation between individuals suffering from diabetes and gum disease. In fact, they both affect each other. This correlation has been termed a TWO-WAY STREET. Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes (consistently elevated blood sugar levels) are at a much greater risk of being diagnosed with gum disease. Individuals with gum disease may encounter issues with their blood glucose management which will aid the advancement of diabetes.
Studies indicate that individuals with uncontrolled diabetes are prone to develop oral health concerns like gingivitis (an early stage of gum disease) as well as periodontitis (severe gum disease). Unmanaged diabetes affects the number of white blood cells individuals need to fend off infections and viruses; this can contribute to the development of severe oral health problems such as gum disease, which is a bacterial attack on the gum tissue. High blood sugar affects the body’s ability to adequately fight off infections, which can lead to infections festering and spreading throughout the mouth and body.
How You Can Help Manage Your Oral Health & Diabetes
For those with diabetes, there is much you can do to lower your risk of developing serious oral health diseases. Ensure that you routinely monitor your blood sugar, take your prescribed medications daily (as specified by your doctor), maintain a healthy diet and establish and exercise. Be sure to brush your teeth at least two times per day and protect the health of your gums by flossing once per day.
Visiting The Dentist Can Positively Impact Oral Health
Visiting your dentist regularly can make a positive difference in the state of your oral health. Making routine trips for dental cleanings and checkups will allow your dentist to track and observe the progress of your oral health and provide them with the knowledge necessary to recommend the treatment needed. Conscientious monitoring of your oral health will only help you control your diabetes.
Oral Health Concerns That Correlate With Diabetes
Here are some oral health signs to look out for if you have diabetes:
- Gums that bleed too easily
- Tender, throbbing or swollen gums
- Pus leaking between the teeth when the gums are compressed
- Persistent bad breath or taste in the mouth
- Extremely dry mouth
- A bite that feels off or different
- Oral candidiasis (thrush)
- Poor or slow healing
Tooth Decay And Tooth Loss
If you have been diagnosed with gingivitis, leaving it untreated can cause periodontal disease. Periodontal disease will negatively impact the bones and gum tissues that hold the teeth in place. With bone loss and deep pockets, there is resultant mobility of teeth and eventually tooth loss. If you have diabetes, the risk of developing the periodontal disease is about three times that of a person without diabetes
Oral Thrush
Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes are also at a higher risk of oral thrush. Oral thrush is caused by a yeast fungus known as, Candida albicans, and although it is present in most people without issue, some people have a much harder time preventing its progression, and it can overtake the mouth. Symptoms of oral thrush may include redness, oral discomfort, cracks at the side of the mouth, etc. Oral examinations performed by dentists can help to identify and diagnose most symptoms of oral thrush.
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Saliva helps break down the foods we eat and assists in washing away leftover remains after meals. Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes often suffer from dry mouth because of dehydration caused by damaged blood vessels and nerves that directly affect salivary production. Another possible reason for dehydration can be attributed to side effects from common medications for type 2 diabetes. When the flow of saliva is decreased, food is often not broken down sufficiently, leaving pieces of debris stagnant in the mouth. Bacteria present within the mouth thrive off the debris, which in turn, creates acid leading to decay. Individuals that are susceptible to dry mouth face a greater risk of tooth decay, cavities, and periodontal disease.
Agape Can Help You
It is imperative that individuals with diabetes, whether managed or unmanaged seek proper oral care. Ensure you schedule regular visits to your dentist. Studies suggest that receiving adequate treatment for gum disease improves blood sugar management for those with diabetes. Make sure to establish proper oral hygiene habits and receive regular deep cleanings to help maintain adequate blood sugar levels and oral health.
Photo source: http://fightgumdisease.com/total-health/diabetes/

